In today's rapidly evolving security landscape, the traditional approach of responding to threats after they occur is no longer sufficient. To ensure the safety and security of individuals and communities within Ghana and Africa, a paradigm shift towards proactive prevention is needed. This article explores the concept of Behavior Threat Detection & Assessment (BTDA) and its potential in moving from response to prevention in the field of security within Ghana and Africa.
1. The Need for Proactive Prevention:
Traditional security measures primarily focus on responding to threats once they have already occurred. However, this reactive approach often falls short in preventing incidents and minimizing their impact. In order to address this gap, a proactive approach is necessary, which involves identifying potential threats before they materialize. BTDA offers a promising solution by focusing on the behavioral indicators that can help detect and assess threats at an early stage.
2. Understanding Behavior Threat Detection & Assessment:
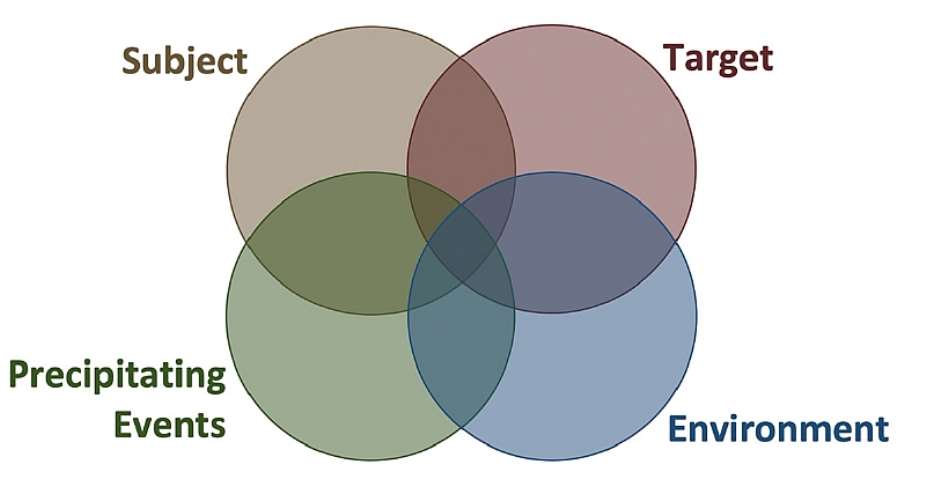
Behavior Threat Detection & Assessment is a multidisciplinary approach that combines behavioral science, data analysis, and technology to identify and assess potential threats based on observable behaviors. By analyzing patterns of behavior, anomalies, and risk indicators, security professionals can proactively detect and assess threats before they escalate into incidents.
3. Behavioral Indicators of Threats:
BTDA relies on identifying and interpreting specific behavioral indicators that may indicate a potential threat. These indicators may include:
a. Unusual or erratic behavior: Individuals exhibiting sudden changes in behavior patterns, such as increased aggression, withdrawal, or extreme emotional states, may raise concerns.
b. Surveillance activities: Suspicious individuals engaging in surveillance activities, such as loitering, taking photographs of critical infrastructure, or conducting reconnaissance, may indicate pre-operational planning.
c. Communication patterns: Monitoring communication channels for indicators of extremist ideologies, violent intentions, or plans to carry out harm can help identify potential threats.
d. Social media monitoring: Analyzing social media posts and interactions can provide insights into individuals or groups expressing extremist views, threats, or plans for violence.
4. Technology and Tools for BTDA:
Advancements in technology have greatly enhanced the capabilities of BTDA. The following tools and technologies are instrumental in implementing effective BTDA systems:
a. Video Surveillance and Analytics: High-resolution cameras coupled with intelligent video analytics can automatically detect suspicious behaviors and trigger alerts for further assessment.
b. Data Integration and Analysis: Integrating data from multiple sources, such as CCTV cameras, access control systems, and social media platforms, enables comprehensive analysis for identifying behavioral anomalies and patterns.
c. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and learn to recognize potential threats more accurately over time.
d. Threat Assessment Software: Specialized software applications can aid in the assessment of potential threats by providing risk scoring, threat categorization, and recommendations for appropriate response measures.
5. Challenges and Considerations:
While BTDA holds great promise, its implementation within Ghana and Africa comes with certain challenges and considerations:
a. Cultural Sensitivity: Behavioral indicators may vary across cultures, and it is essential to develop culturally sensitive frameworks to avoid bias and misinterpretation.
b. Privacy and Ethical Concerns: Collecting and analyzing behavioral data raises privacy and ethical concerns. It is crucial to establish robust frameworks that protect individual rights while ensuring public safety.
c. Training and Expertise: Building the capacity of security professionals in BTDA methodologies and technologies is essential to ensure effective implementation.
d. Collaboration and Information Sharing: Establishing collaboration and information-sharing mechanisms among various stakeholders, including security agencies, private sector organizations, and communities, is crucial for successful BTDA implementation.
Conclusion:
Behavior Threat Detection & Assessment offers a proactive approach to security within Ghana and Africa, shifting the focus from response to prevention. By leveraging behavioral indicators, advanced technologies, and multidisciplinary approaches, BTDA can help identify potential threats at an early stage, enabling proactive intervention and minimizing the risk of incidents. However, it is essential to address challenges, promote collaboration, and ensure ethical implementation to fully harness the potential of BTDA in creating safer and more secure environments within Ghana and Africa.




 Chief Justice recommends five judges for Supreme Court
Chief Justice recommends five judges for Supreme Court
 I was thrown out of my official bungalow, my things thrown into the streets – Na...
I was thrown out of my official bungalow, my things thrown into the streets – Na...
 PURC has become politicised – Nana Yaa Jantuah
PURC has become politicised – Nana Yaa Jantuah
 I’II accept ministerial appointment from Mahama – Former CPP General Secretary
I’II accept ministerial appointment from Mahama – Former CPP General Secretary
 Fetish Priest shoots three persons dead in Tepa-Baniekrom
Fetish Priest shoots three persons dead in Tepa-Baniekrom
 July 3: Cedi sells at GHS15.63 to $1, GHS14.63 on BoG interbank
July 3: Cedi sells at GHS15.63 to $1, GHS14.63 on BoG interbank
 2024 election: Matthew Opoku Prempeh lacks the charisma to bring in floating vot...
2024 election: Matthew Opoku Prempeh lacks the charisma to bring in floating vot...
 HIV breakthrough: drug trial shows injection twice a year is 100% effective agai...
HIV breakthrough: drug trial shows injection twice a year is 100% effective agai...
![Minority Chief Whip, Kwame Agbodza [File Photo]](https://cdn.modernghana.com/content__/84/56/732024115507-1i841p5cbv-agbodza-696x464.jpg) We support LI to regulate cement prices because the issues we raised have been a...
We support LI to regulate cement prices because the issues we raised have been a...
 Ghanaian chef's 'longest cooking marathon' claim hoax
Ghanaian chef's 'longest cooking marathon' claim hoax
